

Diabetes in Dogs
About Glucose Curves
Managing Canine Glucose Curves
The blood glucose curve is an ideal tool to determine the effectiveness of the insulin and identify the appropriate dose and frequency of administration. In general, maintaining blood glucose levels in a dog with diabetes between 100–250 mg/dL for the majority of the day will minimize the symptoms of diabetes and complications.
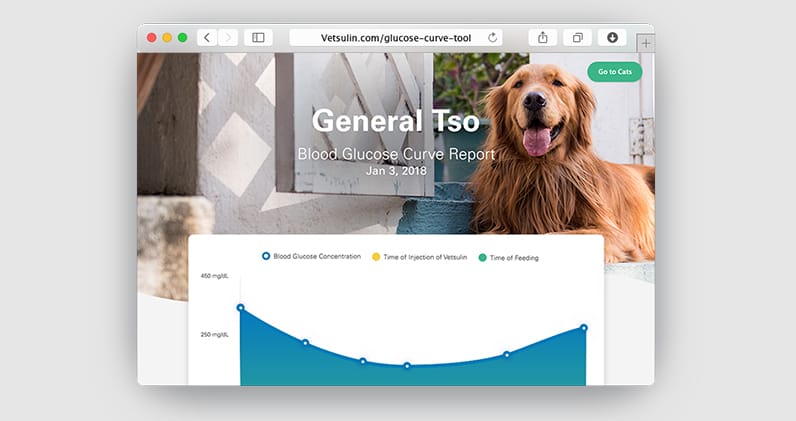
Try our online glucose curve generator
When creating a glucose curve, remember that stress can affect the reliability of results and the glucose curve is only one tool among others that can help manage dogs with diabetes.
How to complete a glucose curve
Feed and inject your dog with Vetsulin® (porcine insulin zinc suspension) as normal. Your veterinarian may suggest you doing this at home, or they will do it at their office. If your dog exercises at home during the day, the same exercise routine should be adhered to while your dog is in the clinic.
Blood sampling:
- Just prior to giving insulin
- Then, in at least 60 to 120 minute intervals
- Over a period of 12 to 24 hours
How to interpret a glucose curve
Your veterinarian can help explain the glucose curve, and how they interpret these readings based on your pet.
The glucose curve helps determine:
- Insulin effectiveness. Maximum and minimum blood glucose levels, which should ideally be between 100 and 250 mg/dL
Glucose nadir (lowest level) goal:
- 100-150 mg/dL
Duration of insulin effectiveness:
- Length of time between the insulin injection and the blood glucose reaching 250 mg/dL
- Duration of effectiveness used to determine frequency of insulin injections
Measuring blood glucose
Two different options:
- Collection by your veterinarian of a venous blood sample from a peripheral vein. These plasma glucose concentrations are measured in a in a laboratory or by an in-clinic analyzer.
- Collection done, at home or in clinic, of a drop of capillary blood from the ear (pinna), or sometimes the inner lip or elbow callus, analyzed with a handheld blood glucose meter (glucometer).
- Glucometers should be calibrated specifically for dogs and cats because of the difference in the ratios of glucose in plasma and red blood cells from humans.
- Readings may vary by as much as 15% from samples submitted to the laboratory.
- Handheld meters are reasonably accurate. If a reading seems unusual or does not match the clinical signs, a second reading should be taken or another method used to confirm the blood glucose measurement.
Management goals
Management of canine diabetes can be considered successful when the clinical signs of diabetes mellitus improve without inducing hypoglycemia.
Routine rechecks
After your dog has been stabilized successfully, your veterinarian may perform routine rechecks every 2–4 months.
Careful monitoring and control will help to limit the long-term complications associated with diabetes.
Blood glucose concentrations
The aim of therapy is to produce a blood glucose curve that approaches the reference range, avoiding potentially fatal hypoglycemia.
An example of a stable dog with diabetes is a blood glucose range of 100–250 mg/dL for most of a 24-hour period.
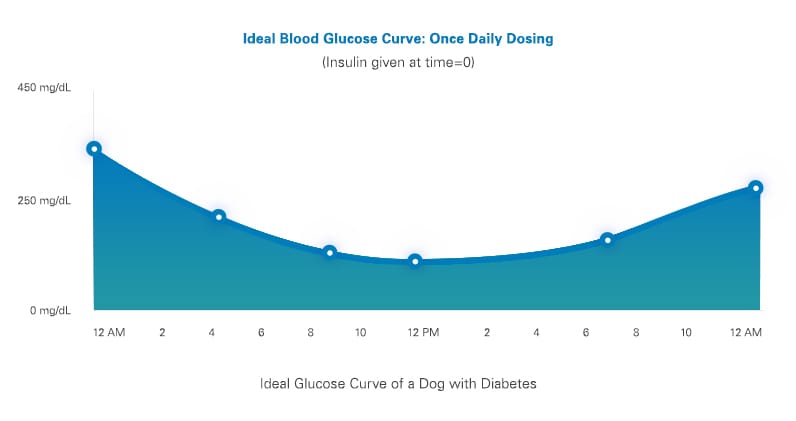
Ideal blood glucose curve
Below is an example of an ideal blood glucose curve for a dog on once-daily dosing where the range remains between 100–250 mg/dL for most of the 24-hour period. Please note that for a dog on twice-daily dosing the curve will appear very similar, but just within a 12-hour time period. Not all blood glucose curves will be ideal at first.
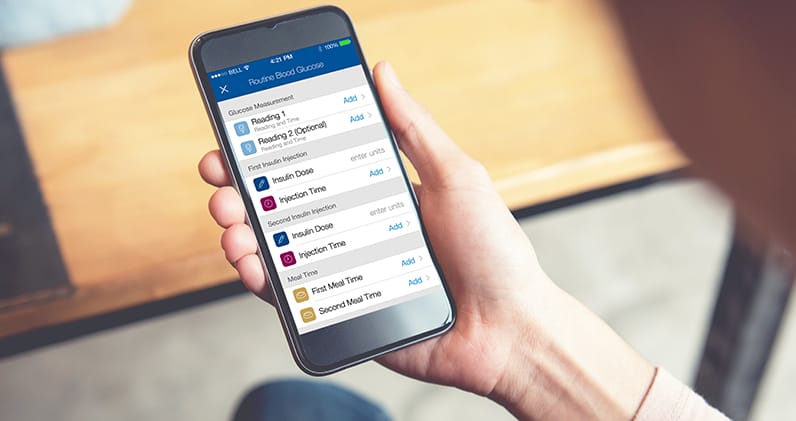
Tracking Results
If you feel your dog is at risk for developing diabetes, consider having your pet tested during a regular veterinary examination at least once a year.
Tracking Tools & Resources
- Pet Diabetes Tracker app
Review and keep important information to manage care. - Blood Glucose Curve Tool
Easily record blood glucose readings to generate a blood glucose curve. - Helpful Downloads
Additional resources to understand and manage canine diabetes.
Further Reading


Talk to Your Vet Today
Find a veterinarian to learn more about pet diabetes, and how cats and dogs can lead a happy, healthy life with proper management.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION:
VETSULIN® and VETPEN® are for use in animals only. Dogs and cats known to have an allergy to pork or pork products should not be treated with VETSULIN®. VETSULIN® is contraindicated during periods of hypoglycemia. Animals with severe ketoacidosis, anorexia, lethargy, and/or vomiting should be stabilized with short-acting insulin and appropriate supportive therapy before use. As with all insulin products, careful patient monitoring for hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia is essential. Overdosage can result in profound hypoglycemia and death. Progestogen and glucocorticoid use should be avoided. The safety and effectiveness of VETSULIN® in puppies, kittens, breeding, pregnant, and lactating dogs and cats has not been evaluated. Keep out of reach of children. Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Accidental injection may cause clinical hypoglycemia. In case of accidental injection, seek medical attention immediately. Exposure to the product may induce a local or systemic allergic reaction in sensitized individuals. For complete safety information, refer to the product label.




