

Diabetes in Dogs
Nutrition for DogsWith Diabetes
Healthy Food Choices
Prescription Diets – These are specially formulated for the management of dogs with diabetes. Diets that contain higher fiber can be particularly useful for helping with weight loss and improving blood sugar control. Ask your veterinarian about the best choices for your dog.
Nonprescription Diets – Diabetes can be managed on a carefully controlled program using their normal diet. It is much easier to manage these plans if a canned food with complete nutrition is used. This method may prove better for fussy eaters, but one should try to avoid diets with high fat content.
Water Consumption – Clean drinking water should be available at all times. A reduction in excessive water consumption is an indicator of successful management of diabetes.
Tips for a Healthy Diet
No matter which diet option you choose, these are the basics for diabetes control:
Consistently feed your dog the same amount of food at the same times each day to avoid unnecessary fluctuations in blood glucose.
Time consistent feedings and insulin treatments so that glucose absorption coincides with peak action of given insulin. (see section below)
Foods high in complex carbohydrates and fiber help glucose to be released evenly in your dog’s body. (High fiber diets are not recommended for underweight dogs. Always ask your veterinarian what is best for your dog.)
Work with your veterinarian to find the correct caloric value to help your dog achieve optimal weight.
Restrict fat in their diet to avoid additional complications.
Timing Meals and Treatments
Your veterinarian will advise you on properly feeding your dog. In general, meals should be timed so that the food in their body coincides with the peak action of the given insulin. This will minimize fluctuations in blood glucose concentrations and, thus, episodes of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
For once-daily insulin injections:
Give the first meal (two-thirds of the daily amount) prior to the morning Vetsulin injection. This allows you to see that your dog is feeling well and eating normally before the insulin is given.
The second meal (the remainder of the daily amount) is usually given about 8-10 hours later.
For twice-daily insulin injections:
As a general rule, feed half of your dog’s total daily food right before or with each injection.
The first meal (half of the daily ration) is given just before the morning insulin injection. This allows you to see that the dog is feeling well and eating normally before the insulin is given.
The second meal (the remainder of the daily ration) is usually given about 10–12 hours later, prior to the second insulin injection.
For specific questions regarding type, volume, timing and frequency of feedings, please consult your veterinarian.

Importance of an Ideal Body Weight
Achieving your dog’s ideal body weight is best for diabetes management. Underweight dogs should avoid high carbohydrates and fiber to best manage diabetes.
For overweight or obese dogs, the goal is controlled weight loss. Overweight dogs can have insulin resistance, which may lead to higher doses being required.
Weight loss should be gradual. Overweight dogs may be fed two-thirds of the recommended daily allowance of a suitable diet until they have reached their ideal body weight. Your veterinarian is the best resource to calculate the ideal body weight and food requirements for your dog with diabetes.
Tracking Results
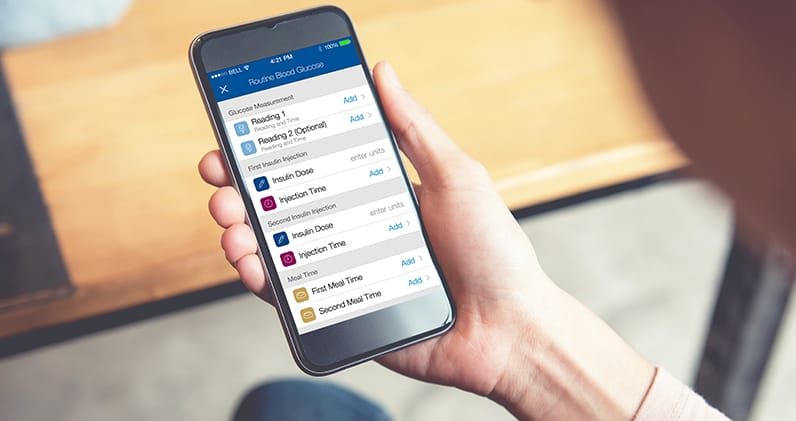
Recording your dog’s results is important to properly manage care.
Tracking Tools & Resources
- Pet Diabetes Tracker app
Review and keep important information to manage care. - Blood Glucose Curve Tool
Easily record blood glucose readings to generate a blood glucose curve. - Helpful Downloads
Additional resources to understand and manage canine diabetes.
Further Reading


Talk to Your Vet Today
Find a veterinarian to learn more about pet diabetes, and how cats and dogs can lead a happy, healthy life with proper management.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION:
VETSULIN® and VETPEN® are for use in animals only. Dogs and cats known to have an allergy to pork or pork products should not be treated with VETSULIN®. VETSULIN® is contraindicated during periods of hypoglycemia. Animals with severe ketoacidosis, anorexia, lethargy, and/or vomiting should be stabilized with short-acting insulin and appropriate supportive therapy before use. As with all insulin products, careful patient monitoring for hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia is essential. Overdosage can result in profound hypoglycemia and death. Progestogen and glucocorticoid use should be avoided. The safety and effectiveness of VETSULIN® in puppies, kittens, breeding, pregnant, and lactating dogs and cats has not been evaluated. Keep out of reach of children. Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Accidental injection may cause clinical hypoglycemia. In case of accidental injection, seek medical attention immediately. Exposure to the product may induce a local or systemic allergic reaction in sensitized individuals. For complete safety information, refer to the product label.




